The Gut Punch Weekly #8
GLP-1 drugs show promise for mental health, Ozempic era sparks next-gen sweeteners, insurer drops weight loss drug coverage, and more!
Top Stories
1) GLP-1 Drugs Show Promise for Mental Health
Researchers identified potential therapeutic applications of GLP-1RAs across multiple neurological and psychiatric domains, with the most promising early evidence emerging for cognitive disorders and substance-use disorders.
The analysis elucidates multiple potential mechanisms of action, including anti-inflammatory effects, dopaminergic pathway modulation, and potential neuroprotective benefits.
While initial safety reviews appear positive, regulatory agencies have recently begun investigating potential neuropsychiatric side effects, including mood changes and suicidal ideation.
(Nature)
2) Ozempic Era Sparks Next-Gen Sweeteners
Oobli, a California-based food tech startup, has raised $18M in Series B1 funding to develop sweet proteins as a zero-glycemic sugar alternative, leveraging precision fermentation to produce proteins like brazzein and monellin that activate sugar taste receptors without impacting blood glucose.
The company has secured FDA approval and is partnering with global ingredient supplier Ingredion to create innovative sweetener solutions.
The startup's sweet proteins can replace over 70% of sugar in products like sodas and baked goods while having no impact on blood sugar, insulin, or gut microbiome, positioning itself at the forefront of the growing $7B sugar alternatives market.
3) Insurer Drops Weight Loss Drug Coverage
Independence Blue Cross (IBX) has restricted coverage of GLP-1 weight loss medications, leaving patients facing potential monthly out-of-pocket costs up to $1,350 for drugs like Wegovy and Zepbound.
The insurer will continue to cover GLP-1 medications only for specific medical conditions such as Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and sleep apnea, citing exorbitant drug costs that could drive up premiums for all customers.
Patients are challenging the insurance company's cost-saving approach, arguing that limiting coverage could lead to higher long-term healthcare expenses by preventing serious health conditions associated with obesity.
(WHYY)
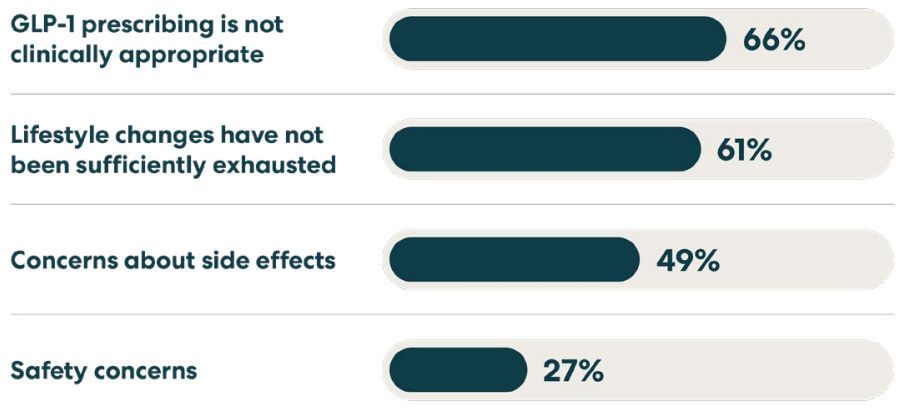
4) Doctors Wary of Telehealth GLP-1 Drug Prescriptions
A survey of 2,000 primary care physicians revealed significant concerns about third-party telehealth providers prescribing GLP-1 medications, with 67% worried about potential health risks and only 18% comfortable with these prescriptions for weight loss.
Physicians are primarily concerned about overprescribing, clinically inappropriate prescribing, and lack of continuity of care, with 57% cautioning patients against using third-party telehealth services for GLP-1 prescriptions.
Most primary care doctors (53%) require patients to attempt non-pharmacological approaches before prescribing GLP-1 medications and believe these drugs should be paired with diet and exercise for effective weight loss.
GLP-1 Industry Intel
Axplora Invests €50M in Advanced Drug Manufacturing: CDMO Axplora is investing €50 million to enhance its Mourenx facility for manufacturing GLP-1 therapies and antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), targeting operational readiness by 2026.
Weight Loss Ad Drives 650% Traffic Spike, Draws Backlash: Hims & Hers' provocative Super Bowl commercial targeting Big Pharma and promoting alternative weight loss medications generated unprecedented engagement and triggered a heated debate about drug marketing and compounding practices.
Websites Falsely Claim FDA Approval for Compounded Drugs: A study revealed that over a third of websites selling compounded GLP-1 weight loss and diabetes drugs falsely claim FDA approval, misleading consumers about medication safety and efficacy.
Potential Medicare Coverage Signals Insurance Shift: A potential Medicare and Medicaid expansion of GLP-1 medication coverage could signal a significant shift in obesity treatment accessibility, with experts predicting that private insurers will follow Medicare's lead.
AI Platform Connects Sleep Apnea and GLP-1 Treatment: Wesper's study reveals how obesity, age, and gender significantly impact sleep apnea metrics, providing critical insights for personalized treatment – especially for patients using GLP-1 medications.
Food & Wellness Industry Intel
Coca-Cola Confident Despite Tariffs and Weight Loss Drugs: Coca-Cola downplayed potential threats from aluminum tariffs and GLP-1 drugs, emphasizing their ability to pivot packaging strategies and maintain sales momentum.
GLP-1 Drugs Boost Pharmacy Sales, Threaten Grocery: Major retailers like Kroger and Walmart anticipate GLP-1 drugs will boost pharmacy sales while potentially reducing grocery spending as GLP-1 users shift away from processed foods and towards more nutrient-dense items.
Weight Loss Drugs Shrink Restaurant Sales: GLP-1 weight loss drugs like Ozempic are potentially disrupting restaurant revenues by reducing customers' food and alcohol consumption, forcing the industry to reconsider portion sizes and dining experiences.
Weight Loss Drugs Reshape Snack Industry Strategy: As GLP-1 medications impact food consumption patterns, snack producers are exploring new strategies like creating nutrient-dense products, stimulating consumer curiosity, and aligning with the 'food as medicine' trend to remain competitive.
GLP-1 Medications Reshape Food Product Development: As GLP-1 medication usage grows, food manufacturers are adapting product strategies by increasing protein, focusing on portion control, and emphasizing savory flavors to meet the changing dietary needs of users.
New App Offers Holistic Weight Loss Telehealth Solution: Claya introduced a digital wellness platform that combines GLP-1 medications, virtual medical consultations, and personalized lifestyle coaching to help individuals achieve sustainable weight loss.
Frontline Focus
GLP-1 Drugs May Impact Libido in Unexpected Ways: GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic may impact libido differently for individuals, with some experiencing increased sexual desire due to weight loss and improved physical comfort while others report decreased sex drive.
Workers Prioritize Weight-Loss Drug Health Coverage: A new survey reveals that weight-loss drug coverage like Ozempic is becoming increasingly important for workers, with 73% considering it a key factor in job retention and 31% willing to change jobs for coverage benefits.
Patients Risk Unsafe Weight-Loss Drugs Online: Patients seeking cheaper weight-loss drugs through telehealth platform Zappy Health discovered serious safety concerns after receiving medications from an unlicensed compounding pharmacy, Ousia, which lacked critical sterile production certification.
FDA Warns of Dangerous Counterfeit Weight Loss Drugs: As GLP-1 weight-loss drugs gain popularity, the FDA is alerting users to the dangers of counterfeit medications being sold through unverified online channels.
Obesity Costs Employers Billions in Hidden Expenses: Canadian obesity experts warn employers that failing to comprehensively address obesity in benefits plans could lead to significant economic losses through increased healthcare costs, reduced productivity, and employee well-being challenges.
GLP-1 Clinical Insights
Ozempic Shows Promise in Reducing Alcohol Cravings: A groundbreaking study reveals that semaglutide could potentially reduce alcohol cravings by 30%, opening new possibilities for addiction treatment research.
GLP-1 Drugs Show Promise for Lung Health: Researchers found that diabetes medications like GLP-1 and SGLT-2 might help reduce inflammation and improve respiratory outcomes for patients with type 2 diabetes and COPD.
GLP-1 Drugs Show Promise for HIV Heart Failure: A comprehensive analysis found that among HIV and heart failure patients, being underweight is more dangerous than being mildly obese, and emerging medications offer significant mortality reduction, particularly for patients in higher weight categories.
Diabetes Drug Effectiveness Varies with Patient Age: Age significantly impacts the effectiveness of diabetes drugs, with SGLT2 inhibitors showing better cardiovascular protection but reduced glycemic control in older patients, while GLP-1 receptor agonists demonstrate improved blood sugar management but less heart health benefits.
Alternative GLP-1 Dosing May Cut Costs: Mathematical modeling suggests alternative dosing regimens for GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide and tirzepatide could potentially reduce medication costs while maintaining significant weight loss efficacy.
Bariatric Surgery Outperforms Meds in Liver Disease: Researchers found that bariatric surgery was associated with lower mortality and fewer major adverse cardiac events than GLP-1 and SGLT-2 medications in metabolic liver disease patients.
The Bleeding Edge
Oral Drug Delivery Faces Major Scientific Challenges: Researchers identify major obstacles in oral drug delivery, including limited gut targeting, absorption challenges for biologics, and insufficient predictive research models.
Anti-Activin Antibody Boosts Muscle and Bone Health: A novel study demonstrates that targeting activin receptors with a specific antibody can promote muscle hypertrophy, enhance bone formation, and potentially offer therapeutic benefits for age-related muscle and bone loss.
Liraglutide and HIIT Protect Heart in Diabetic Rats: Researchers found that liraglutide and HIIT together provide superior cardiac protection in diabetic rats by improving heart structure, reducing fibrosis, and mitigating the progression of heart failure.
Time-Restricted Feeding Alters Gut Bacteria and Appetite: A study on pigs revealed that time-restricted feeding promotes GLP-1 secretion and regulates appetite by enhancing Lactobacillus colonization and tryptophan metabolism.