The Gut Punch Weekly #26
Lilly's antibody preserves muscle, Novo Nordisk ends Hims deal, China approves first dual GLP-1/GCG obesity drug, and more!
Top Stories
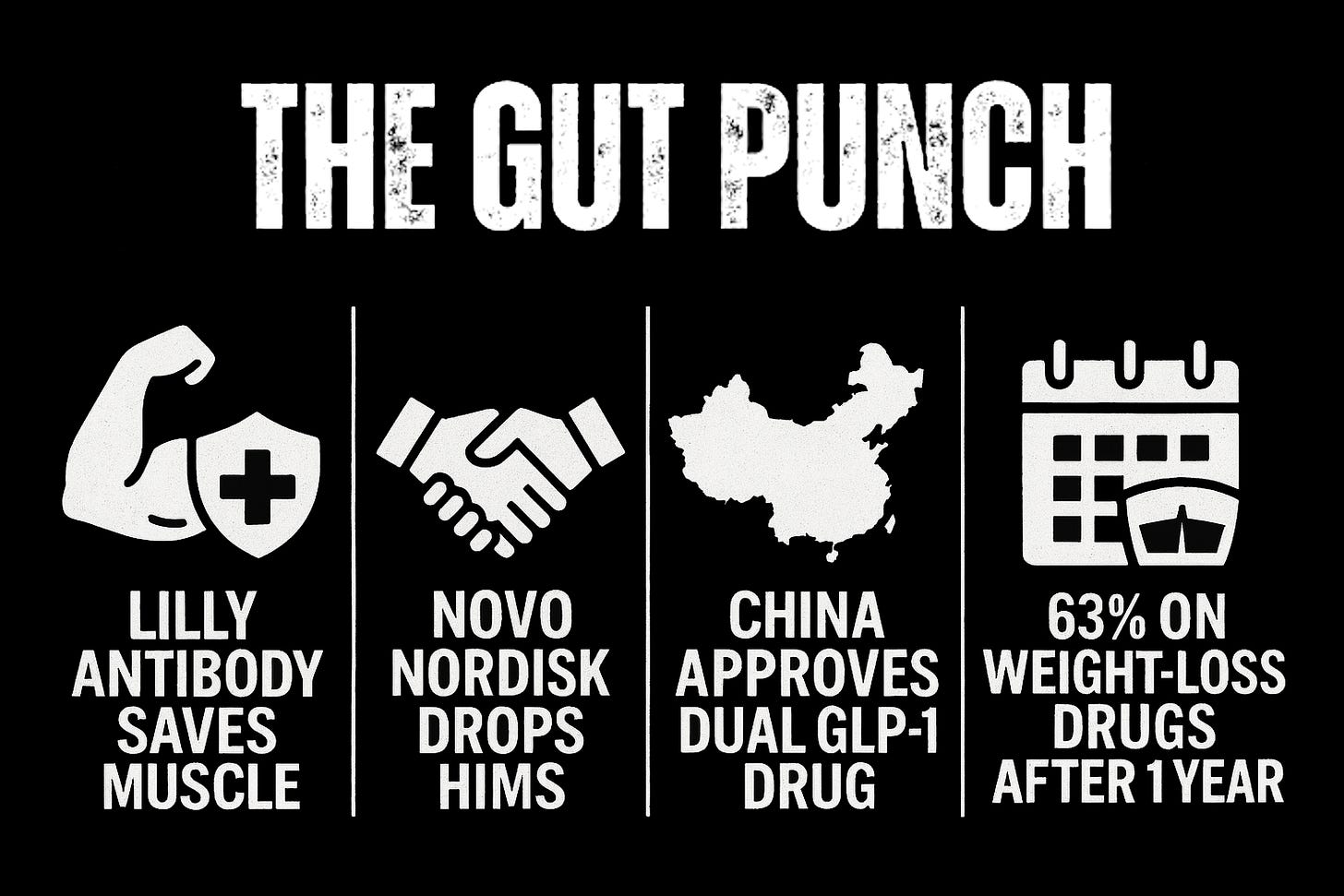
1) Lilly's Antibody Preserves Muscle in Weight Loss with Wegovy
Eli Lilly’s investigational antibody bimagrumab, when combined with Novo Nordisk’s semaglutide (Wegovy), enables patients to lose significant weight while preserving far more muscle mass compared to semaglutide alone.
In the Phase IIb BELIEVE study, the combo led to 22.1% weight loss over 72 weeks, with 92.8% of the reduction coming from fat and a 67% relative increase in preserved lean muscle versus semaglutide alone.
While the results are robust and position Lilly ahead of competitors in the muscle-preserving weight loss space, some safety concerns arose such as observed elevations in certain liver and pancreatic enzymes.
(Biospace)
2) Novo Nordisk Ends Hims Deal Over Compounded Drug Sales
Novo Nordisk terminated its partnership with Hims & Hers to sell Wegovy through the telehealth platform, citing concerns over the company's continued sale of compounded GLP-1 drugs.
This decision led to a 30% plunge in Hims & Hers stock.
Novo Nordisk accused Hims & Hers of engaging in illegal "sham compounding" and disseminating deceptive marketing that puts patient safety at risk.
Hims & Hers CEO Andrew Dudum refuted Novo Nordisk's claims, stating the company was being pressured to steer patients towards Wegovy regardless of clinical appropriateness.
Dudum asserted that Hims & Hers will continue to offer a range of weight loss treatments, including Wegovy, to ensure patient choice.
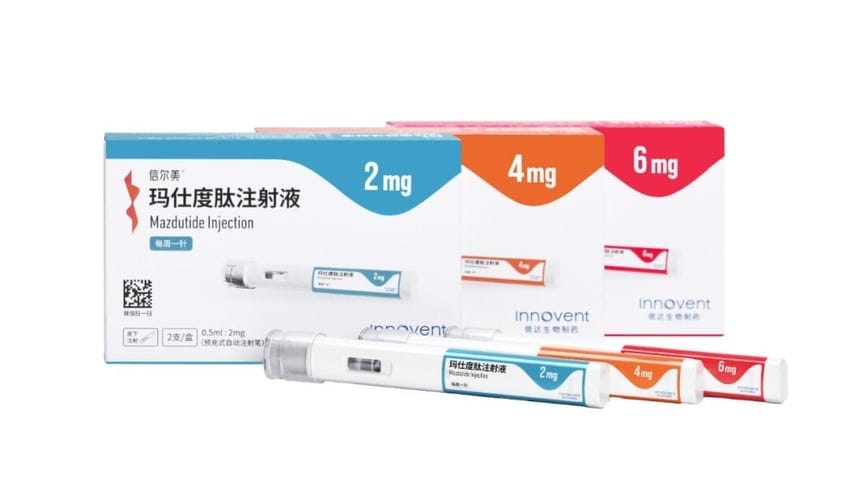
3) China Approves First Dual GLP-1/GCG Obesity Drug Class
China's NMPA has approved mazdutide, the world's first dual GLP-1/glucagon receptor agonist for chronic weight management in adults with obesity or overweight plus a weight-related comorbidity.
Developed by Eli Lilly and licensed to Innovent Biologics for China, mazdutide showed significant weight loss efficacy in the GLORY-1 phase 3 trial, with up to 14.8% average weight reduction at 48 weeks.
The approval marks a breakthrough for incretin medicines and addresses China's growing obesity epidemic, though mazdutide will face competition from established GLP-1 drugs like Wegovy and Zepbound.
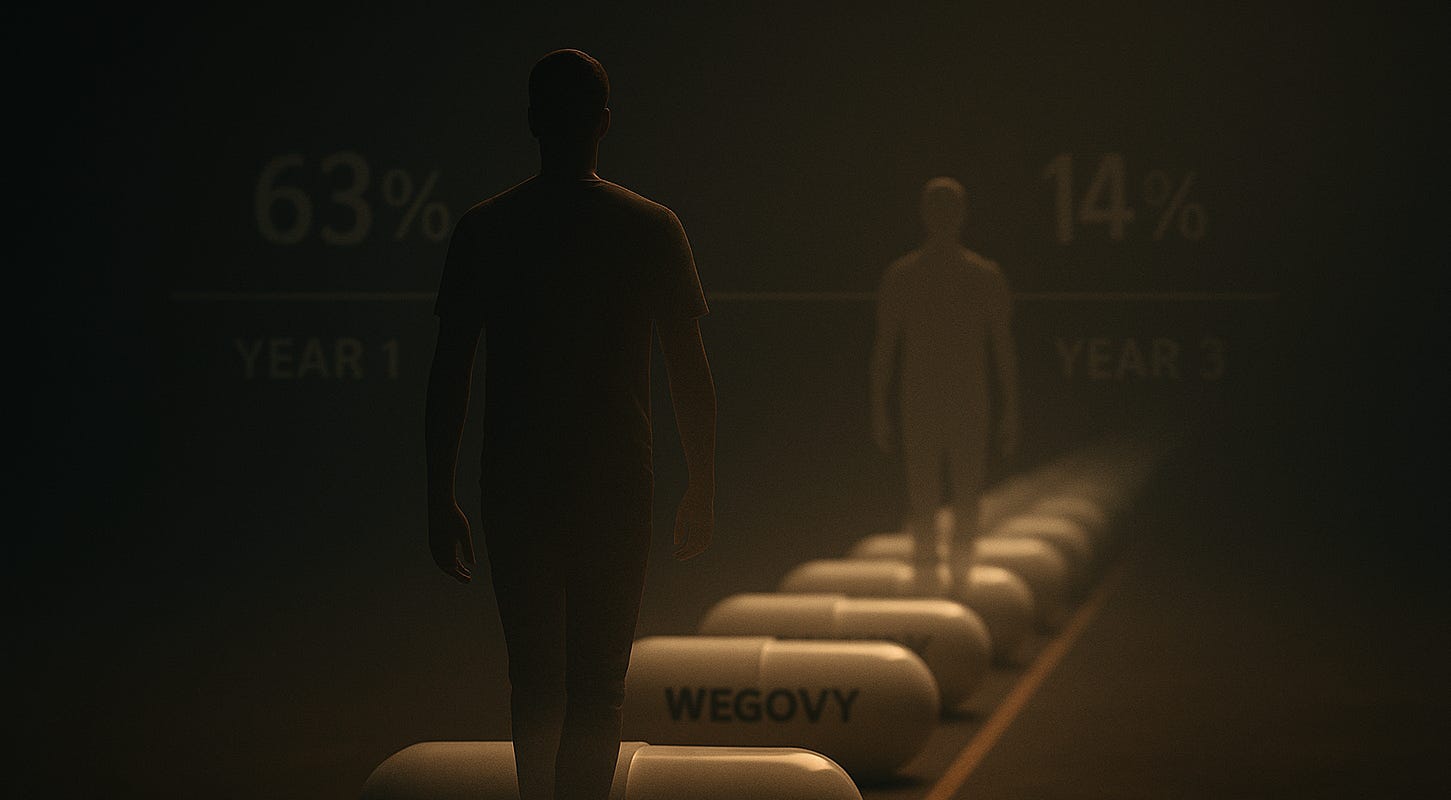
4) Most Patients Now Stay on Weight Loss Drugs
Persistence on popular weight-loss drugs Wegovy and Zepbound has risen sharply, with 63% of US patients staying on therapy for a year -- up from 40% for Wegovy starters in 2023.
Experts attribute improved adherence to easing supply shortages, broader insurance coverage, and better management of side effects.
However, longer-term retention remains low, with only 14% on Wegovy after three years.
Employers and payers continue to weigh the high upfront costs against uncertain long-term savings, as ongoing use appears necessary to sustain weight-loss benefits.
(Reuters)
GLP-1 Industry Intel
Altimmune Stock Plummets on Mixed Liver Drug Trial Results: Altimmune’s pemvidutide achieved MASH resolution and weight loss goals in Phase IIb trials but failed to improve fibrosis, leading to a 53% stock drop.
WeightWatchers Partners with Novo Nordisk for Wegovy Access: WeightWatchers will offer Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy for weight loss starting July 1 through a new partnership aimed at expanding access and streamlining delivery for consumers.
Supply and Pricing Missteps Cost Novo Market Share: Despite early indicators of massive demand for Wegovy, Novo Nordisk's leadership maintained conservative forecasts and pricing strategies, leading to supply shortages and market share losses to competitor Eli Lilly.
China's Ecnoglutide Matches Wegovy in Weight Loss Study: A late-stage study shows China's Sciwind Biosciences' experimental weight loss drug ecnoglutide achieved 10-15% body weight reduction, comparable to Novo Nordisk's Wegovy.
Lilly's Oral GLP-1 Pill Matches Injectable Diabetes Drugs: Lilly's once-daily oral GLP-1 drug orforglipron demonstrated significant A1C reductions of 1.3% to 1.6% and weight loss up to 16 pounds in Phase 3 trial results for type 2 diabetes patients.
MindRank's Oral GLP-1 Drug Shows 10% Weight Loss Potential: MindRank's oral GLP-1 drug MDR-001 demonstrated promising phase 2b trial results with up to 10.3% weight loss after 24 weeks, showing comparable efficacy to Eli Lilly's orforglipron.
Zealand's Obesity Drug Shows Over 11% Weight Loss: A Phase Ib study of Zealand's dapiglutide showed promising 11.6% weight reduction, with analysts noting the unique GLP-2 component could help address inflammation-related comorbidities.
Food & Wellness Industry Intel
Weight Loss Drugs Shift Alcohol Consumption Habits: GLP-1 weight loss drugs are reducing alcohol cravings and shifting drinking habits, prompting alcohol brands to adapt to a new era of more intentional, health-focused consumption.
Frontline Focus
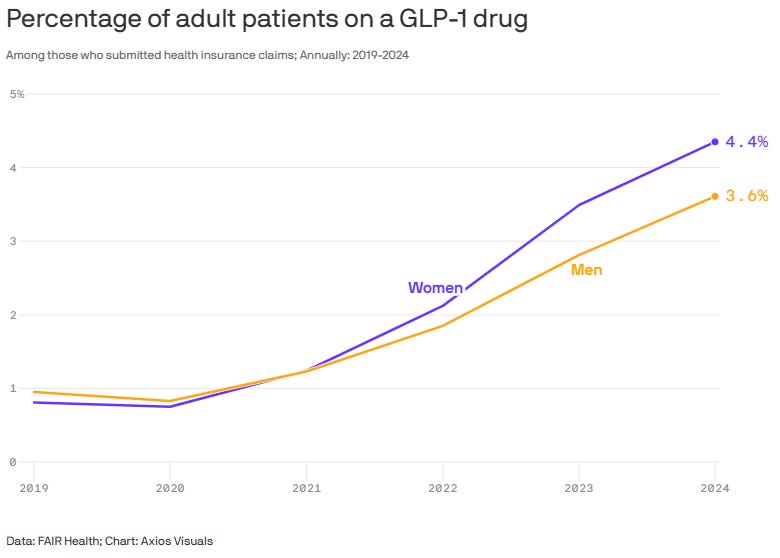
Perimenopausal Women Drive Surge in GLP-1 Prescriptions: Women, especially those approaching menopause, are driving the surge in GLP-1 weight-loss prescriptions, with women over 40 far outpacing men in off-label use for obesity.
Real-World GLP-1 Weight Regain Less Than Clinical Trials: Real-world patients who discontinue GLP-1 weight loss medications experience less dramatic weight regain compared to clinical trial participants, according to Cleveland Clinic research.
Americans Turn to DIY Weight Loss Drug Market: Americans are turning to a growing 'gray market' for weight-loss drugs, importing cheap active ingredients from China and mixing their own injectable medications to avoid high prescription costs.
Luxury Wellness Retreats Adapt to Ozempic Era: Luxury wellness retreats are evolving to support clients using weight loss drugs like Ozempic, offering tailored programs to address new challenges such as muscle loss, side effects, and long-term health habits.
GLP-1 Clinical Insights
GLP-1 Drugs Effective for Childhood Obesity: A meta-analysis of 11 trials found GLP-1 receptor agonists significantly reduce weight and BMI in children and adolescents with obesity, including those under 12.
GLP-1 Drugs Show Promise in Treating Substance Use Disorders: Recent research, including a VA study of nearly two million individuals, suggests GLP-1 medications may help reduce substance use disorders through effects on reward processing and stress regulation.
Semaglutide May Reduce Alcohol Consumption and Cravings: New research indicates that GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide may help reduce alcohol consumption and cravings in people with alcohol use disorder (AUD), independent of weight loss effects.
Telehealth Boosts Access to Alcohol Treatment with Naltrexone: Telehealth platforms are increasing access to naltrexone, a medication for alcohol use disorder, by reducing stigma and making treatment more convenient and patient-centered.
New Chinese Obesity Drugs Rival Western Competitors: Chinese pharmaceutical companies Corxel and Sciwind have reported promising weight loss data for their respective GLP-1 drugs, with Corxel's oral candidate showing up to 9.7% weight reduction and Sciwind's injectable ecnoglutide achieving 15.4% loss in clinical trials.
Tirzepatide Lowers Calorie Intake by Reducing Food Cravings: A 6-week clinical trial found that tirzepatide significantly reduced food intake and appetite in overweight adults, potentially by affecting brain regions associated with food reward and cravings.
The Bleeding Edge
FGF21 Plus GLP-1 May Help Reduce Alcohol Cravings: A new study shows that a synthetic version of the liver hormone FGF21, especially when combined with GLP-1 drugs, could help treat alcohol use disorder by reducing alcohol consumption and cravings in male mice.
Broad Bean Protein Enhances Hormonal Control of Blood Sugar: New research reveals that broad bean albumin 1b (BA1b) improves glucose metabolism in diabetic mice by promoting the secretion of GIP and GLP-1 through upregulation of VDAC1 gene expression.