The Gut Punch Weekly #24
GLP-1s elevate eye disease risk, Lilly and Camurus partner on long-acting obesity drugs, GLP-1s linked to unexpected pregnancies, and more!
Top Stories
1) Study Links GLP-1 Drugs to Higher Eye Disease Risk
A major new study found that diabetes patients using GLP-1 drugs are twice as likely to develop neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD), a serious eye disease that can lead to rapid vision loss.
Although the absolute risk remains low, the study adds to growing concerns about potential ocular side effects of GLP-1 therapies, which have also been linked to rare cases of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION).
In response to these concerns, the European Medicines Agency's safety committee recently recommended updating product information for semaglutide to include NAION as a "very rare" side effect.
2) Lilly and Camurus Partner on Long-Acting Obesity Drugs
Eli Lilly has partnered with Camurus in a deal worth up to $870 million to develop long-acting versions of GLP-1 and other incretin-targeting drugs for obesity and diabetes treatment.
Camurus' technology allows for the creation of long-acting injectables that can provide sustained drug release for days, weeks, or months.
This partnership could help Lilly counter the threat of competitors developing less frequently dosed therapies.
Camurus' delivery technology involves a lipid-based liquid that forms a crystalline gel inside the body after injection, slowly releasing the active ingredient over time.
Lilly can apply Camurus' technology to up to four compounds, including dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonists, triple GIP, glucagon and GLP-1 receptor agonists, and potentially amylin receptor agonists.
(BioSpace)
3) GLP-1 Drugs Linked to Unexpected Pregnancies
The UK's Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has issued a warning about unintended pregnancies in women using GLP-1 weight loss drugs like Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro.
These medications may interfere with the absorption of oral contraceptives by slowing digestion, potentially reducing their effectiveness.
The MHRA has recorded 40 pregnancy reports linked to these drugs, with 26 specifically associated with Mounjaro.
Doctors caution that these medications are not intended for cosmetic weight loss and advise women using GLP-1 drugs to use additional contraception if pregnancy is not desired.
(VICE)
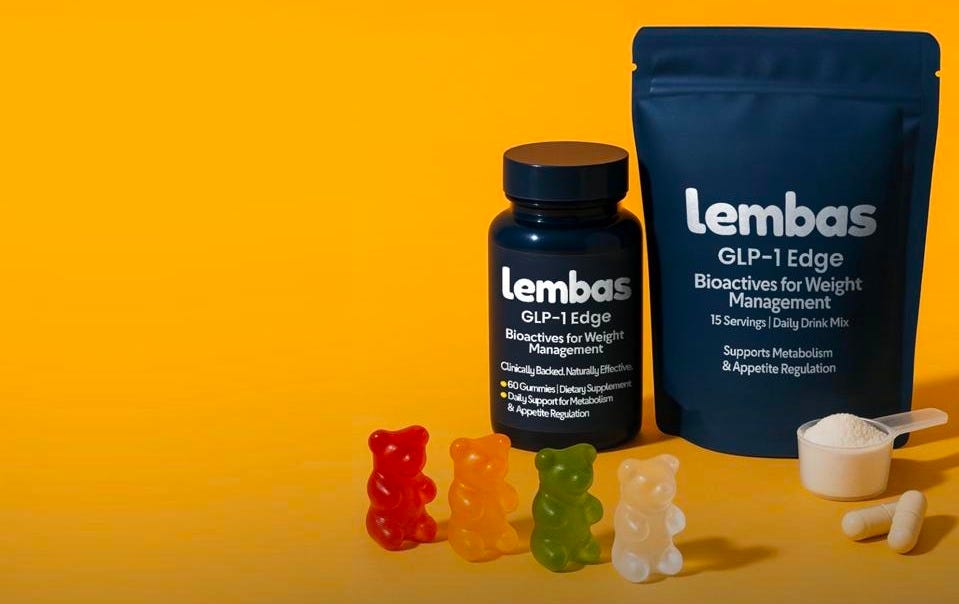
4) Lembas Raises $3.6M for Food-Based GLP-1 Alternative
Lembas, a new peptide ingredient company, has entered the market with $3.6 million in pre-seed funding to create GLP-1 Edge, a powder that can be added to food products for weight loss.
Their product targets the same pathway as pharmaceutical GLP-1 agonists, but through food consumption rather than injections.
The company plans to conduct clinical trials and then partner with CPG brands to incorporate GLP-1 Edge into various food products, such as yogurt, protein bars, and gummy bears.
Lembas claims the ingredient won't affect taste and can help consumers lose 10-15% of their body weight in about two months.
(Forbes)
GLP-1 Industry Intel
Metsera's Amylin Drug Shows Promising 8.4% Weight Loss: Metsera's amylin analog achieved 8.4% placebo-adjusted weight loss after 36 days in Phase 1 trials, potentially supporting monthly dosing and combination therapy with their GLP-1 drug candidate.
Omada Health IPO Soars Amid GLP-1 Drug Interest: Virtual healthcare platform Omada Health is going public with a $1.08 billion market cap, leveraging growing interest in weight management fueled by GLP-1 drugs.
Activist Fund Targets Novo Nordisk Amid CEO Search: Activist hedge fund Parvus Asset Management is building a stake in Novo Nordisk and seeks to influence the appointment of a new CEO following the company's 50% share price decline.
Lilly Launches App to Support Zepbound and Mounjaro Users: Eli Lilly and Welldoc are expanding their partnership with a new app that helps Zepbound and Mounjaro users track their medications and health data while managing cardiometabolic conditions.
Lilly Halts Telehealth Sales of Copycat Weight-Loss Drugs: Eli Lilly announced it will only be partnering with telehealth companies that agree to stop selling compounded versions of weight-loss drugs, potentially imperiling their deal with Hims & Hers.
Food & Wellness Industry Intel
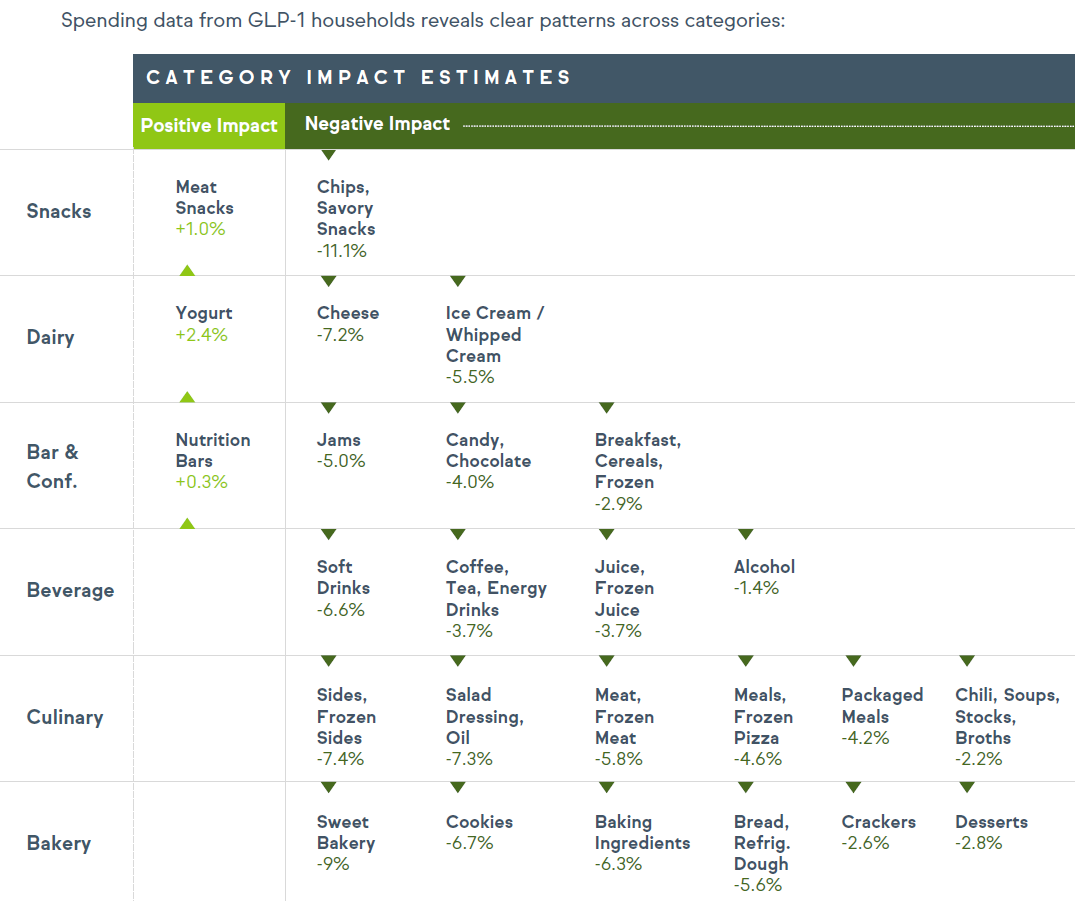
Weight Loss Drugs Change How Americans Taste Food: According to new IFF research, GLP-1 weight loss drugs are dramatically altering food preferences and taste perceptions, with 85% of users reporting major changes in their eating habits.
Starbucks Tests Protein Cold Foam to Boost Health Appeal: Starbucks is testing protein-infused cold foam in response to growing consumer demand for protein-rich beverages, particularly among health-conscious customers and those using GLP-1 medications.
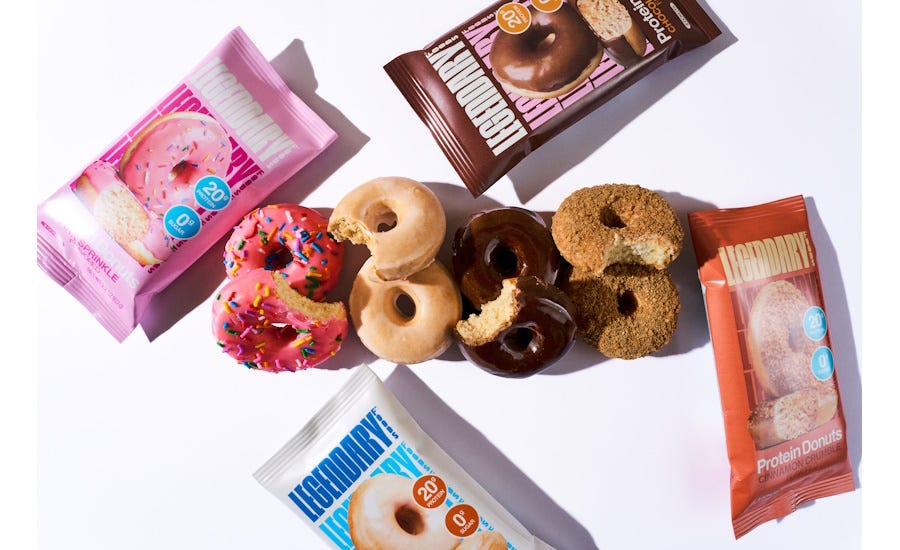
Legendary Foods Launches Zero-Sugar, High-Protein Donuts: Legendary Foods expands its high-protein snack portfolio with new sugar-free, protein-based donuts in four flavors.
Weight Loss Drugs Trigger Sell Rating for McDonald's: McDonald’s shares dropped after an analyst issued a rare sell rating, citing concerns that weight-loss drugs like GLP-1s and inflation could reduce fast-food sales and revenue.
Overall Meat Consumption Surges as Plant-Based Alternatives Decline: The meat industry is experiencing a renaissance as consumers, particularly men and Gen Z, embrace meat products for their protein content while moving away from processed meat alternatives.
Protein Shakes Popular with Ozempic Users Deemed Unhealthiest Drink: Core Power protein shakes, popular among Ozempic users, were ranked America's unhealthiest bottled drink due to high sugar, processed ingredients, and potential health risks.
Frontline Focus
Medicare Negotiates Lower Drug Prices Including Ozempic: Medicare has begun its second round of drug price negotiations with pharmaceutical companies, including discussions for 15 medications such as Ozempic, with new prices set to take effect in 2027.
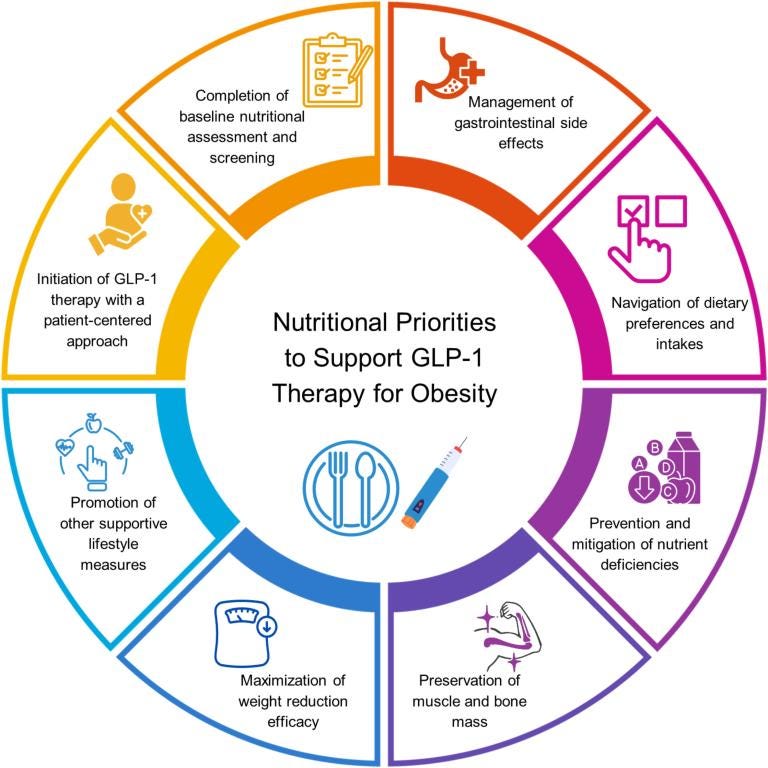
GLP-1 Weight Loss Drugs Need Nutrition Support: Long-term success with GLP-1 weight loss drugs requires integrating nutrition and lifestyle interventions to prevent side effects, maintain muscle and bone mass, and sustain healthy weight loss.
AI Tech Cuts GLP-1 Authorization Time by 83%: Electronic prior authorization (EPA) technology is streamlining GLP-1 medication approvals by integrating with electronic health records and using AI, reducing turnaround times by 83% and submission times by 10 hours.
GLP-1 Clinical Insights
Real-World Weight Loss Drug Results Less Effective Than Trials: Cleveland Clinic found patients on injectable obesity drugs lost less weight in real-world use than in clinical trials, mainly due to treatment discontinuation and lower maintenance doses.
Weight Loss Drug Tirzepatide Works Differently in Mice, Humans: Research published in Cell Metabolism demonstrates that tirzepatide causes weight loss in mice by preventing metabolic adaptation and increasing fat oxidation, while in humans it primarily works by reducing caloric intake.
GLP-1 Users Advised to Fast 24 Hours Before Anesthesia: New consensus guidelines recommend patients on GLP-1 medications should fast from solid foods for 24 hours before anesthesia rather than stopping their medications.
GLP-1 Drugs Significantly Reduce Kidney Disease Risk: A meta-analysis of 19 trials found GLP-1 receptor agonists reduce kidney disease risk by 19% and offer substantial renal and cardiovascular benefits.
The Bleeding Edge
CBL-514 Targets Weight Rebound Post-GLP-1 Treatment: New preclinical data suggests Caliway's CBL-514 drug could prevent post-treatment weight regain in GLP-1 patients through targeted fat reduction.
GLP-1 Brain Signaling Essential for Metabolic Control: A new study reveals that GLP-1 regulates a crucial brain circuit between the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus and dorsal vagal complex that controls feeding behavior and energy balance in mice.