The Gut Punch Weekly #16
Pfizer halts obesity drug due to safety concerns, Zepbound users maintain weight loss over three years, FDA seizes hundreds of counterfeit Ozempic doses, and more!
Top Stories
1) Pfizer Halts Obesity Drug After Liver Safety Concerns
Pfizer has discontinued development of its oral GLP-1 receptor agonist danuglipron after a patient experienced potential drug-induced liver injury in a phase 1 trial, eliminating the centerpiece of Pfizer's obesity treatment pipeline.
Pfizer previously had to discontinue development of another compound, lotiglipron, due to elevated liver enzyme levels.
Pfizer still has an oral small molecule GIPR antagonist in phase 2 development for obesity, but plans for a combination therapy with danuglipron are now off the table.
Pfizer's discontinuation of its weight-loss drug danuglipron boosted shares of competitors Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly as they look set to retain their dominance in the obesity drug market.
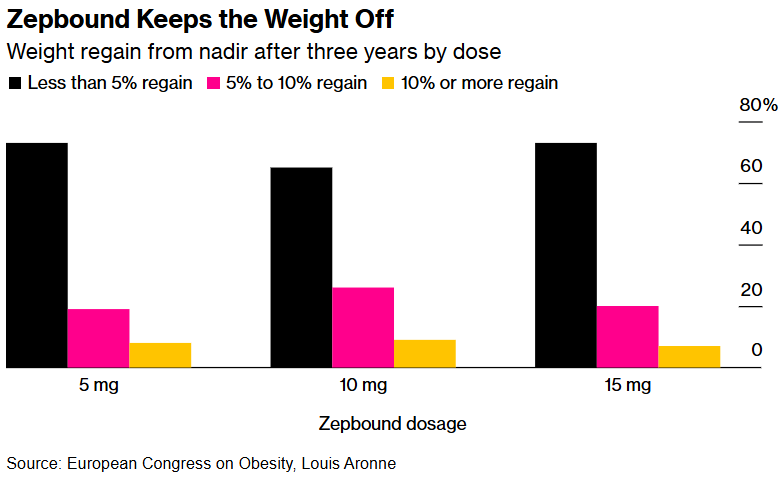
2) Long-Term Weight Loss with Zepbound Proven Over Three Years
A three-year study of Zepbound, Eli Lilly's obesity medication, shows that patients taking the drug consistently kept most of the weight off for at least three years, with most regaining only 5% or less of their initial weight loss.
The research indicates that Zepbound may be more effective than other interventions, such as bariatric surgery, in maintaining weight loss over time.
However, the study also emphasizes the importance of continued use, as stopping the medication can lead to substantial weight regain.
While the drug shows promise, real-world challenges such as supply shortages, side effects, and lack of insurance coverage have made it difficult for some patients to maintain consistent use.
3) FDA Seizes Hundreds of Counterfeit Ozempic Doses
Novo Nordisk, the manufacturer of Ozempic, notified the FDA on April 3 about counterfeit 1-milligram injections being distributed outside its authorized supply chain in the U.S.
The FDA urges patients and doctors to verify the legitimacy of their Ozempic prescriptions.
The counterfeit products are distinct from compounded versions of the drug, which gained in popularity during last year's semaglutide shortage.
In February, the FDA announced that shortages of Ozempic and Wegovy had been resolved in the U.S., effectively ending the sale of less expensive compounded versions of these drugs.
(NBC News)
4) Study Shows Ozempic Users Cut Calories, Choose Better Foods
A study by Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station found that people taking GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic tend to reduce consumption of sugary soft drinks, beef, and processed foods.
The study also noted increased consumption of fruits, leafy greens, and water among users, suggesting a shift towards healthier dietary choices.
Researchers estimate that people taking GLP-1 drugs consume 720 to 990 fewer calories than before treatment, demonstrating the medications' strong weight loss potency.
Despite reduced consumption, users still reported high desire for calorie-dense foods, suggesting GLP-1 drugs may alter taste sensitivity or pleasure response to food rather than completely eliminating cravings.
This insight could help the food industry shift food product development and marketing strategies to cater to the changing dietary preferences of GLP-1 users.
The food industry is already responding to the impact of GLP-1 drugs, with some companies launching less sugary products aimed at users of these medications.
(Gizmodo)
GLP-1 Industry Intel
Tirzepatide Surges Ahead in Diabetes and Obesity Care: New research shows tirzepatide – the first medication targeting multiple incretin pathways for diabetes and obesity – has rapidly gained traction, accounting for 31.1% of weight-loss prescriptions by December 2023.
Investors Bet Big on Chinese Obesity Drug Pipeline: Led by serial biotech entrepreneur Ron Renaud, Kailera secured $400 million from venture capital firms to develop four Chinese-licensed obesity drugs, including a potentially best-in-class GLP-1 therapy that showed promising weight loss results in early trials.
Goldman Sachs Cuts Weight-Loss Drug Market Projections: Wall Street's weight-loss drug enthusiasm is cooling as analysts predict steeper price drops and market fragmentation despite Eli Lilly’s maintained growth potential.
Nurx Partners with Gifthealth to Streamline Zepbound Access: Women's healthcare company Nurx teams up with Gifthealth to improve access to Zepbound weight management medication, targeting the 66% of adult women affected by obesity or overweight conditions.
Food & Wellness Industry Intel
WeightWatchers Files Bankruptcy as Ozempic Reigns Supreme: WeightWatchers, once valued at $6 billion in 2018, is preparing to file for bankruptcy as consumers abandon dieting in favor of pharmaceutical solutions like Ozempic.
GLP-1 Users Maintain Healthy Habits Post-Medication: According to Acosta Group's GLP-1 Shopper Community study, although most consumers cease GLP-1 medication early due to cost and side effects, these users often maintain improved dietary habits and seek healthier food options.
GLP-1 Patients Choose Premium Fast Food Options: Revenue Management Solutions' research shows GLP-1 medication users are visiting restaurants more frequently than non-users, particularly favoring QSRs for their convenience, controlled portions, and nutritional transparency.
Supplement Market Targets Consumers Cycling Off GLP-1 Drugs: Supplement companies see opportunities to serve consumers who cycle off expensive GLP-1 medications, particularly with products addressing muscle mass loss, though they must avoid making claims that mimic pharmaceutical properties.
GLP-1 Drugs Reshape Food and Pharma Packaging Demand: The rise of GLP-1 drugs is reshaping the packaging industry, boosting demand for pharmaceutical packaging and prompting food packaging manufacturers to innovate
Rousselot Debuts Nextida Collagen for Glucose Control: Rousselot will soon unveil Nextida GC, a clinically-studied collagen peptide composition designed to regulate glucose levels naturally through GLP-1 response.
Frontline Focus
RFK Jr. Considers GLP-1 Coverage Framework for Medicare/Medicaid: HHS Secretary RFK Jr. is considering a framework for Medicare and Medicaid coverage of GLP-1 weight loss drugs, but only after patients try other interventions like glucose monitors and lifestyle change
Off-Label Use of GLP-1 Drugs Rises Among Type 1 Diabetics: GLP-1 drug use among type 1 diabetes patients has increased 800% over the past decade despite limited safety and efficacy data.
Online Black Market for Weight-Loss Drugs Expands Rapidly: As legitimate access to popular weight-loss drugs tightens, patients are turning to potentially dangerous alternatives including compounded medications and unregulated research peptides.
Insurers Struggle with High Costs of Obesity Medications: While GLP-1 drugs are cost-effective in the long run, their high prices and expansive eligibility have been causing insurers to limit coverage among the most vulnerable populations.
Fashion Industry Reverses Course on Body Diversity: Fashion's body positivity movement has suffered a reversal, with reports showing substantial decreases in plus-size model representation across major fashion weeks.
Compounded GLP-1 Drugs Ban Sparks Transition Challenges: As compounded GLP-1 drugs phase out, healthcare providers are exploring various strategies to help patients maintain weight loss, including slow tapering, lifestyle changes, and transitions to generic medications.
GLP-1 Clinical Insights
GLP-1 Agonists Enhance Gut Microbiome Health: A comprehensive review suggests that GLP-1 medications like semaglutide and liraglutide may improve metabolic health by fostering growth of beneficial gut bacteria while suppressing harmful microbes.
Strength Training, Protein Key to Minimize Muscle Loss on GLP-1s: Under obesity specialist supervision, patients using GLP-1 drugs experienced substantial fat loss while maintaining most muscle mass through strength training and protein-rich diets.
GLP-1 Drugs Counteract Weight Regain After Bariatric Surgery: A new study shows GLP-1 receptor agonists effectively combat post-bariatric surgery weight regain, with patients losing nearly all regained weight after 12 months of treatment.
GLP-1 Drugs Offer Hope for Lymphedema After Cancer: A groundbreaking case study suggests that GLP-1 weight loss drugs like Zepbound and Wegovy may effectively treat lymphedema in breast cancer survivors.
The Bleeding Edge
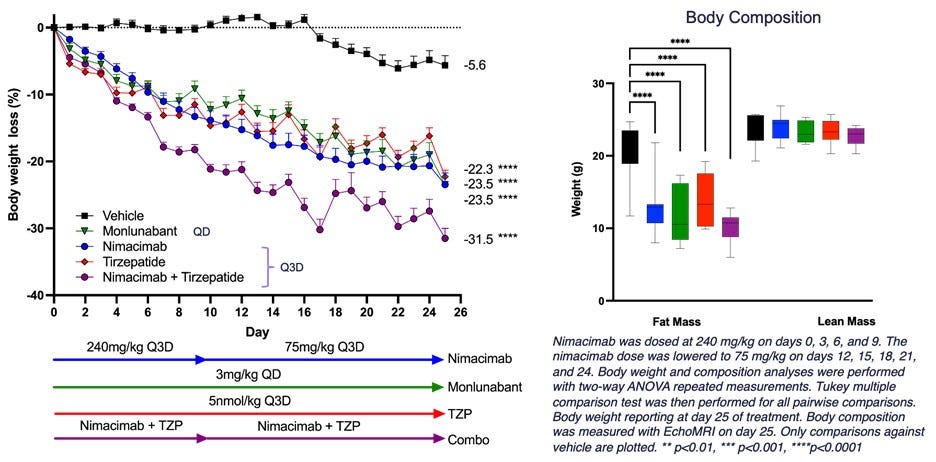
Nimacimab Plus Tirzepatide Achieves 30% Weight Loss in Study: Skye Bioscience's novel CB1 antibody nimacimab achieved 23.5% weight loss alone and over 30% when combined with tirzepatide in preclinical studies.